- C++
离散化算法-区间和
- @ 2024-1-6 16:52:44
区间和


离散化算法重点 离散化是一种将连续变量转换为离散变量的技术。在数据分析和机器学习中,离散化通常用于将连续变量转换为有意义的类别或区间。以下是在C++中实现离散化的知识点和代码示例:
知识点:
- 离散化是将连续变量转换为离散变量的过程。
- 离散化的方法包括阈值法、聚类法等。
- 离散化对于数据分析和机器学习任务中的分类、聚类和决策树等算法非常有用。
2 条评论
-
 mrhowe SU @ 2024-1-7 20:41:02
mrhowe SU @ 2024-1-7 20:41:02#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N = 1e6+10; int aw[N],aq[N],n,m; vector<int> alls,a1,a2,b1,b2; int find(int x) { //返回的是输入的坐标的离散化下标 int l = 0, r = alls.size() - 1; while (l < r) { int mid = l + r >> 1; if (alls[mid] >= x) r = mid; else l = mid + 1; } return r + 1; } int main(){ cin>>n>>m; int x,c,l,r; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ cin>>x>>c; a1.push_back(x); a2.push_back(c); alls.push_back(x); } for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ cin>>l>>r; b1.push_back(l); b2.push_back(r); alls.push_back(l); alls.push_back(r); } sort(alls.begin(),alls.end());//排序 alls.erase(unique(alls.begin(),alls.end()),alls.end());//去重 for(int i=0;i<=a1.size()-1;i++){ int wz = find(a1[i]); aw[wz] = a2[i]; } //前缀和 for (int i = 1; i <= alls.size(); i++) aq[i] = aq[i-1] + aw[i]; for(int i=0;i<=b1.size()-1;i++){ cout<<aq[find(b2[i])]-aq[find(b1[i])-1]<<endl; } return 0; } -
 @ 2024-1-6 17:08:13
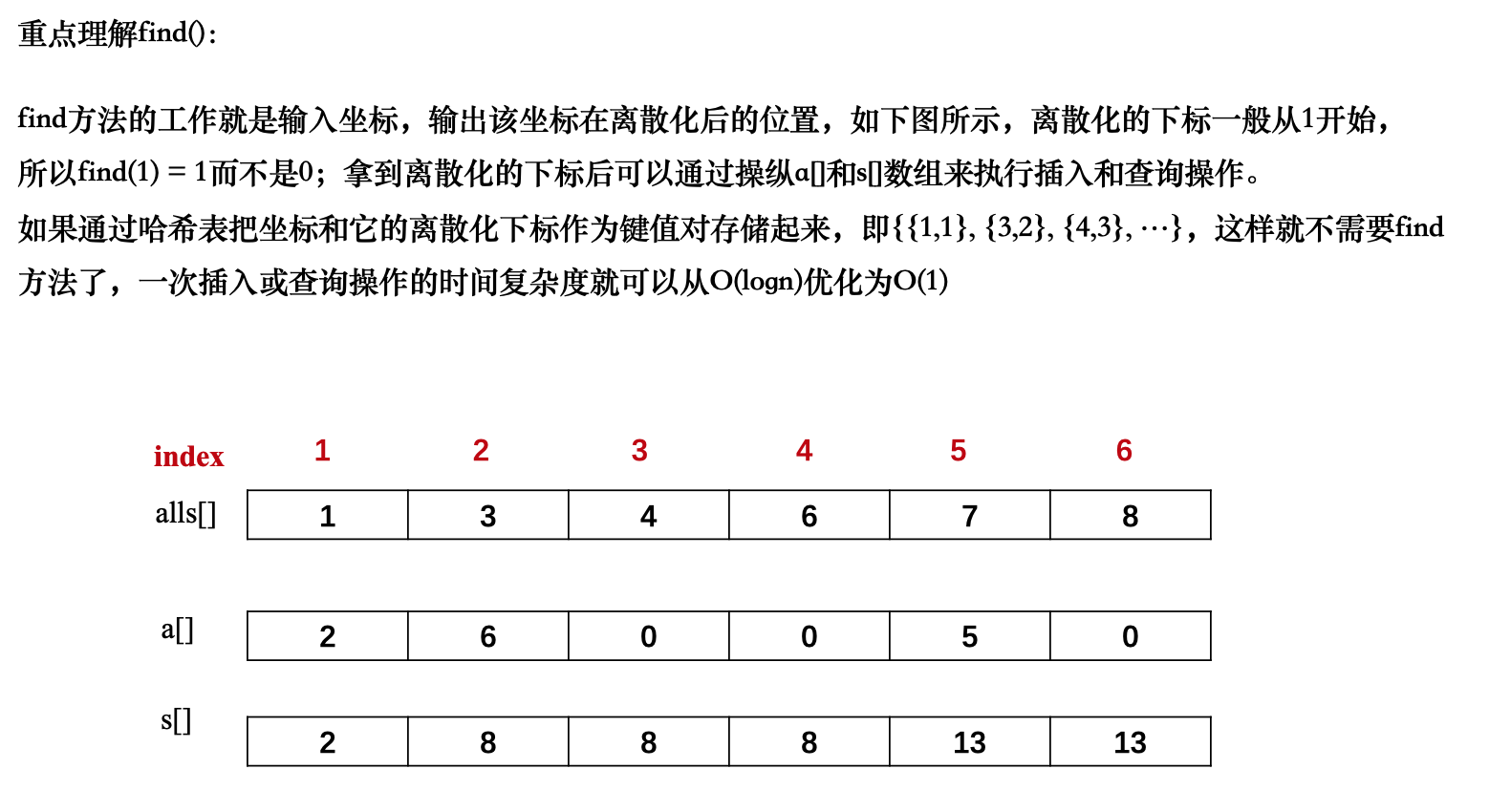
@ 2024-1-6 17:08:13#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int N = 300010; //n次插入和m次查询相关数据量的上界 int n, m; int a[N];//存储坐标插入的值 int s[N];//存储数组a的前缀和 vector<int> alls; //存储(所有与插入和查询有关的)坐标 vector<pair<int, int>> add, query; //存储插入和询问操作的数据 int find(int x) { //返回的是输入的坐标的离散化下标 int l = 0, r = alls.size() - 1; while (l < r) { int mid = l + r >> 1; if (alls[mid] >= x) r = mid; else l = mid + 1; } return r + 1; } int main() { scanf("%d%d", &n, &m); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { int x, c; scanf("%d%d", &x, &c); add.push_back({x, c}); alls.push_back(x); } for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { int l , r; scanf("%d%d", &l, &r); query.push_back({l, r}); alls.push_back(l); alls.push_back(r); } //排序,去重 sort(alls.begin(), alls.end()); alls.erase(unique(alls.begin(), alls.end()), alls.end()); //执行前n次插入操作 for (auto item : add) { int x = find(item.first); a[x] += item.second; } //前缀和 for (int i = 1; i <= alls.size(); i++) s[i] = s[i-1] + a[i]; //处理后m次询问操作 for (auto item : query) { int l = find(item.first); int r = find(item.second); printf("%d\n", s[r] - s[l-1]); } return 0; }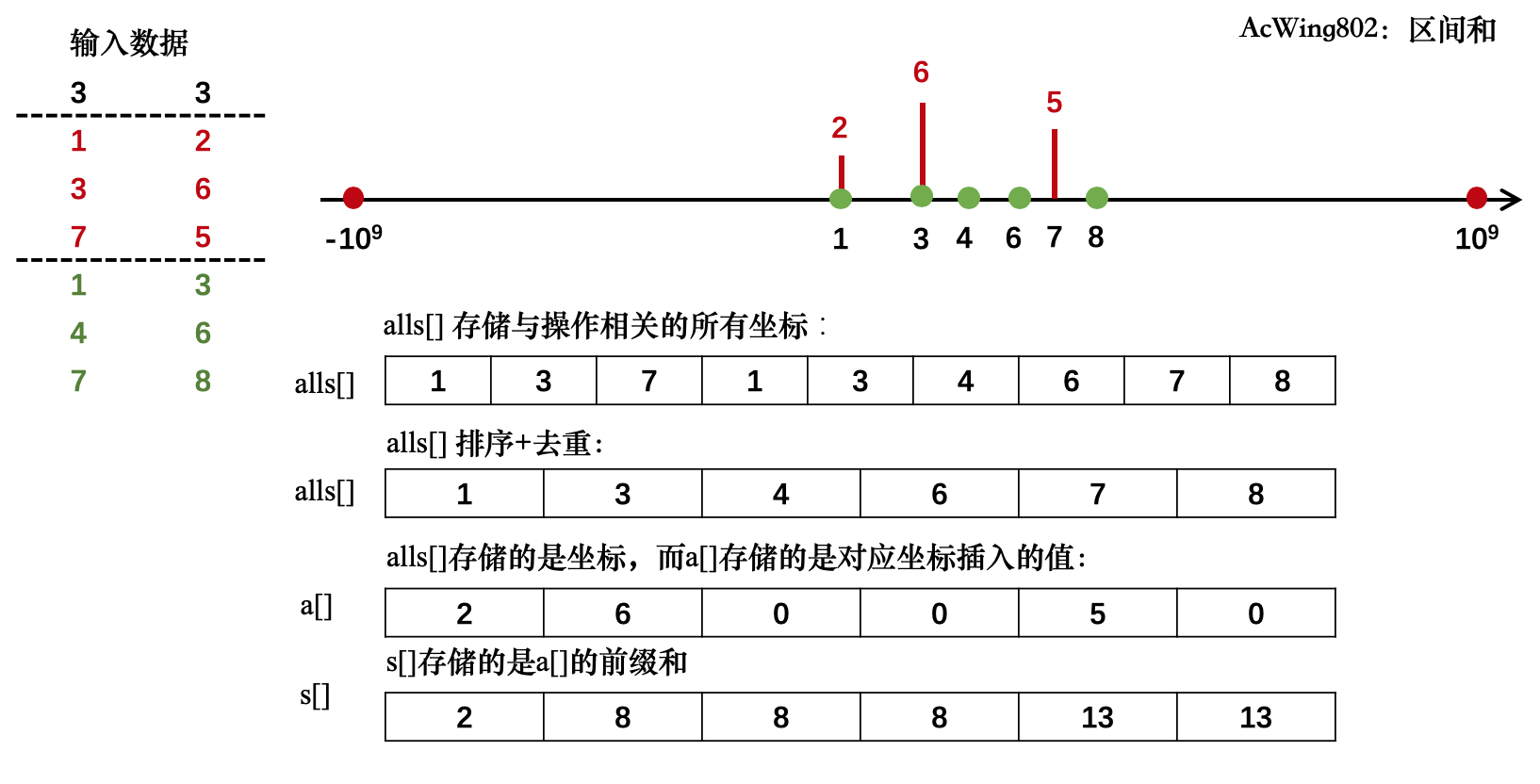
- 1
